Dermatitis
Introduction
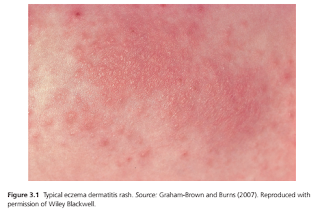
Dermatitis is characterized by sore, red, itching skin.
In primary care, the two most common forms of dermatitis are irritant and allergic dermatitis.
Management
Most cases of mild-to-moderate atopic eczema, irritant and allergic dermatitis should respond to skin care and treatment with OTC products.
- Emollients are the key to managing eczema.
- These preparations should be thought of as indefinite treatment and to be used as often as needed to keep the skin hydrated and moist.
- To avoid the drying effects of soap, a soap substitute should be used.
- Topical corticosteroids
- Patient should be instructed to use a fingertip unit.
- Topical corticosteroids should be applied liberally, not sparingly, to areas of inflamed skin until the skin is completely clear.
- Patients and parents should be reassured that the benefits outweigh the harms and they should not be afraid to use them.
- Antihistamines
- Antihistamines have limited therapeutic benefit for most type of dermatitis. However, a sedating antihistamine at bedtime may improve sleep in an itchy patient.
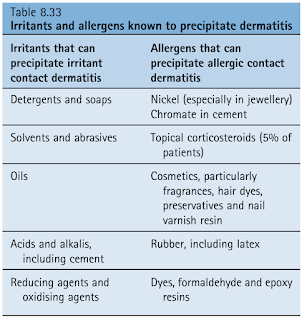
- Avoidance of aggravating or precipitating factors.
- May refer to a dermatologist for patch testing.
- Sweating intensified the itching, so strategies to keep the person cool will help; cotton and loose-fitting clothing can be worn.
Comments
Post a Comment