Morning Sickness
Introduction
Primary nausea and vomiting in pregnancy is a common condition affecting 70-85% of women, with varying degrees of nausea and/or vomiting, typically occurring in early pregnancy.
- It is sometimes misleading called morning sickness as it actually can occur at any time during the day.
- Nausea and vomiting are common in the first pregnancy than in subsequent ones.
Hyperemesis gravidarum is the term used to describe the severe end of the symptom spectrum (including weight loss exceeding 5% of pre-pregnancy body weight).
Symptoms
Nausea and vomiting usually begin around week 6 and resolve around week 14 of gestation, so symptoms can generally be expected to improve around the end of the first trimester.
- In a minority of women, nausea and vomiting may be sufficiently severe to require hospital admission for correction of dehydration and electrolyte imbalances (hyperemesis gravidarum).
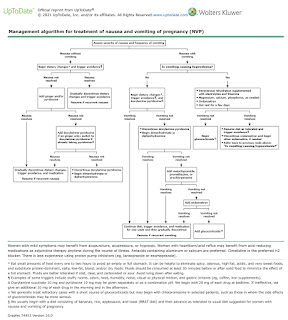
Nondrug Management
Nausea and vomiting during pregnancy can often be effectively managed with nondrug therapy.
Reassurance of a good prognosis and dietary modification may be sufficient.
- Eating small, frequent, high-carbohydrate, low-fat meals
- Changing to a multivitamin without iron*
- Maintaining adequate hydration with cold drinks or ice chips as tolerated
- Snacking on high-protein foods between meals
- Eating crackers or plain biscuits before getting out of bed in the morning
- Avoiding spicy foods and strong odours.
Other nondrug therapies include
- Adequate sleep
- Acupressure or acupuncture may be helpful
- Ginger may be considered
* Women with iron-deficiency anaemia should not discontinue iron supplements, though an alternative method of administration may be considered. If stopped, iron supplements should be restarted around week 12 of gestation when iron demands increase.
Pharmacologic Therapy
After other causes of nausea and vomiting have been ruled out and trial nondrug therapies for 1 week, may consider pyridoxine alone or in combination with doxylamine as first-line treatment.
NOTE: Safety data in humans about ondansetron in pregnancy are conflicting; a small increase in cardiovascular malformations has been reported.
External Links
- Vitamin B6 is effective therapy for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study, 1991
- Pyridoxine for nausea and vomiting of pregnancy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 1995
- Ondansetron compared with metoclopramide for hyperemesis gravidarum: a randomized controlled trial, 2014
- Use of ondansetron during pregnancy and congenital malformations in the infant, 2014
- Interventions for nausea and vomiting in early pregnancy, 2015
- Interventions for treating hyperemesis gravidarum, 2016
- Association of Maternal First-Trimester Ondansetron Use With Cardiac Malformations and Oral Clefts in Offspring, 2018
Comments
Post a Comment