Acanthosis Nigricans
Introduction
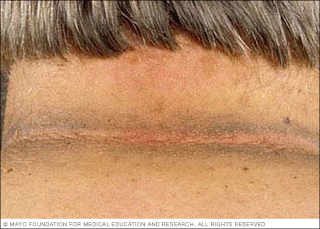
Acanthosis nigricans is a skin disorder characterized by darkening (hyperpigmentation) and thickening (hyperkeratosis) of the skin, occurring mainly in the folds of the skin in the armpit, groin and back of the neck.
- The patches often appear gradually without any other symptoms.
- Sometimes the skin may be itchy.
Aetiology
Most, if not all, patients with acanthosis nigricans have one of the following categories of disorders.
- Obesity
- Endocrine and metabolic disorders, particularly disorders associated with insulin resistance
- Genetic syndromes with acanthosis nigricans
- Familial acanthosis nigricans
- Malignancy
- Drug reactions
- Examples: systemic glucocorticoids, injected insulin, oral contraceptives, niacin, protease inhibitors, palifermin, testosterone, aripiprazole.
NOTE: Although acanthosis nigricans is usually harmless, the prognosis for patients with malignant acanthosis nigricans is often poor since malignancy is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Management
Since acanthosis nigricans is often benign, cosmetic concerns are typically the primary indications for treatment. The preferred method of management is treatment of the underlying cause, when feasible.
- Obesity-related
- Weight loss with diet and exercise
- Drug-induced
- Discontinuation of the inciting drug often results in the resolution of the skin lesion.
- Malignancy associated
- Insulin resistance
- Agents that improve insulin sensitivity, such as metformin, rosiglitazone
Topical therapies that normalize epidermal proliferation, such as topical retinoids and topical vitamin D analogues (calcipotriol), and laser therapy may be of benefit.
- Systemic retinoids (e.g. isotretinoin and acitretin) may lead to clinical improvement in patients with extensive or severe disease, but they have a wide range of potential adverse effects and relapse is common after treatment discontinuation.
Excessive scrubbing of the affected skin during bathing should be discouraged, since it may result in lichenification and worsening hyperpigmentation.
Comments
Post a Comment