Definitions in NICU
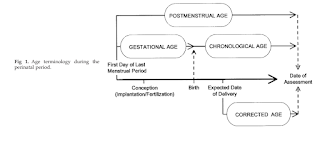
Age Terminology
Neonates - babies from birth to the age of 30 days of postnatal life, including both preterm and post-term babies.
Gestational age (GA) - the age from the time of conception to birth, expressed in completed weeks.
Chronological age or postnatal age (PNA) - the time elapsed after birth, expressed in days, weeks, months or years.
Post-menstrual age (PMA) - is the sum of gestational age and chronological age, usually expressed in weeks.
Example: A preterm infant born at a gestational age of 33 weeks who is currently 10 weeks old (chronological age) would have a postmenstrual age of 43 weeks.
Corrected age or adjusted age - a term most appropriately used to describe children up to 3 years of age who were born preterm. This term represents the age of the child from the expected date of delivery. Corrected age is calculated by subtracting the number of weeks born before 40 weeks of gestation from the chronological age.
Example: A 24-month-old, former 28-week gestational age infant has a corrected age of 21 months.
Preterm Classifications
Preterm - babies born alive before 37 weeks of pregnancy are completed.
Moderate-to-late preterm (LPT) - babies who are 32 weeks to less than 37 weeks of gestational age.
Very preterm (VPT) - babies who are 28 weeks to less than 32 weeks of gestational age.
Extremely preterm (EPT) - babies who are less than 28 weeks of gestational age.
Classification by Birth Weight
Low birth weight (LBW) - less than 2500 g.
Very low birth weight (VLBW) - less than 1500 g.
Extremely low birth weight (ELBW) - less than 1000 g.
Appropriate for gestational age (AGA) - babies born at the appropriate weight for their gestational age (10th-90th percentile).
Large for gestational age (LGA) - babies who weight more than expected for their gestational age. This condition is commonly caused by maternal diabetes (>90th percentile).
Small for gestational age (SGA) - babies who weigh less than expected for their gestational age (<10th percentile).
Obstetric History Classifications
Obstetric history is expressed in gravida/para/abortus (GPA).
Gravida - the total number of times a woman has been pregnant regardless of whether those pregnancies were carried to term.
Para - the number of viable births.
Abortus - the number of pregnancies that were lost for any reason, including miscarriages.
When a woman has not had any pregnancy loss, history may be expressed simply as gravida/para (GP). For example, a woman who was pregnant 3 times, who gave birth to 2 infants and suffered 1 miscarriage, would be expressed G3-P2-A1. A woman who had 4 pregnancies and 4 live births and no abortions or miscarriages would be expressed G4-P4.
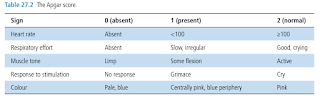
APGAR Scoring System
APGAR (Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity and Respiration) scoring for each category is numerical from 0 to 2, with 0 as the least responsive and 2 as the healthiest response.
- Appearance includes observations such as colour of the extremities and the rest of the body.
- Grimace refers to response to stimulation.
- Activity refers to muscle tone.
This evaluation is performed on the infant at 1, 5 and 10 minutes of life. A total score ranging from 7 to 10 indicates the baby's condition is normal. Scores of 0 to 3 are low and indicate that immediate medical intervention is required.
Comments
Post a Comment