Nausea and Vomiting
Introduction
Nausea (the desire to vomit) and vomiting are common occurrences that can be caused by
- Simple disease, e.g. after exposure to bacterial toxins
- Motion sickness
- More serious underlying pathology
Management
When vomiting is undesirable, the first approach is to remove any precipitating factor if possible.
- In cases of infection, food poisoning, or alcohol intoxication, vomiting may be considered an appropriate physiological response to eliminate noxious agents.
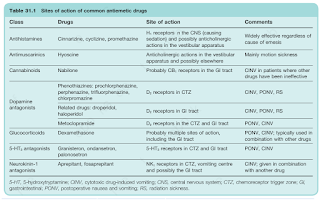
- Not all antiemetics are effective for all conditions, e.g. serotonin and dopamine receptor antagonists are ineffective in motion sickness.
- If a patient does not respond to an antiemetic, trial a different antiemetic. Some antiemetics have multiple mechanism of action, so it may be appropriate to trial a different drug from the same class.
Drug choice considerations
- Betahistine, which is a histamine analogue, is relatively contraindicated in patients with asthma and peptic ulceration.
- The older, sedating antihistamines and the antimuscarinic agents may cause unwanted antimuscarinic side effects such as blurred vision, urinary retention and constipation.
- Phenothiazines (including prochlorperazine), cinnarizine and metoclopramide may cause extrapyramidal effects. These agents may also uncover or worsen existing Parkinson's disease. These effects are far less common with domperidone, which does not penetrate the blood brain barrier extensively.
- Nonetheless, domperidone should be avoided in patients with conduction disorders or cardiac disease due to its association with Q-T interval prolongation.
- If nausea and vomiting does not respond to the therapies above, consider other drugs such as
- Mirtazapine - may be useful for nausea and vomiting associated with functional dyspepsia or gastroparesis.
- Olanzapine - may be useful for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
Summary
Regardless of the cause of vomiting, rehydration therapy can be initiated to replenish the fluid and electrolyte loss.
Comments
Post a Comment