External Storage
Introduction
External storage devices have come a long way since the clunky days of floppy disks.
- Today, we have a diverse array of options at our disposal, each with its own unique strengths and limitations.
Floppy Disks (Diskette)
The floppy disk was the first removable storage medium that many people experienced, particularly during the era of early personal computers.
- Despite their limited storage capacity of 1.44 MB, they were revolutionary at the time, enabling users to store and transfer data more easily.
However, their meagre storage space quickly rendered them obsolete as newer technologies emerged.
- Even so, the floppy disk continues to be the iconic symbol of "SAVE" in word processing software.
Optical Discs: Compact Disks and Digital Versatile Disks (CDs and DVDs)
Before the internet became readily available and USB flash drives dominated the scene, CDs and DVDs were the primary media for storing large amounts of data, such as music albums, movies, software and games.
- These optical discs offered capacities of up to 700 MB (CDs) and 4.7 GB (DVDs), a significant leap from floppy disks.
- Both CDs and DVDs came in rewritable and non-rewritable formats, but scratches could easily damage the data stored on them.
While they are still used for some purposes, the rise of streaming services (e.g. Netflix and Disney+) and the increased adoption of thinner, lighter laptops have led to a decline in their usage.
USB Flash Drives
In the age of digital files, USB flash drives remain a popular choice for storing and transporting documents, photos, music and other files. This enduring popularity stems from several factors:
- Staggering capacities now reaching 2 TB (and beyond),
- Their compact size that fits easily in your pocket,
- Relative affordability compared to other storage options, and
- The ease of use with their plug-and-play functionality.
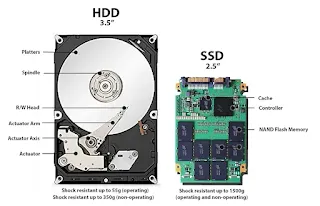
Hard Disk Drives and Solid-State Drive (HDDs and SSDs)
Despite being bulky, HDDs offer massive capacities at relatively affordable prices, making them ideal for storing large files.
Instead of using spinning disks, SSDs utilize flash memory, resulting in significantly faster data transfer speeds, quieter operation and improved durability.
- However, the higher cost per gigabyte of SSDs, compared to HDDs, make them a less budget-friendly option.
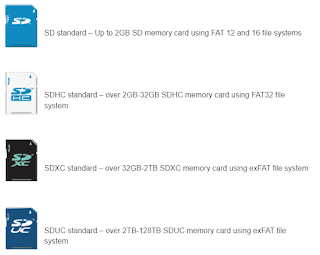
Secure Digital (SD) and microSD cards
For storing data in compact devices like cameras, smartphones and gaming consoles, SD and microSD cards are the go-to solution.
- These tiny flash-based storage devices offer a good balance between size and capacity.
- While microSD cards are smaller than their SD counterparts, both use the same electrical connections, allowing microSD cards to be used in SD-compatible devices with an adaptor.
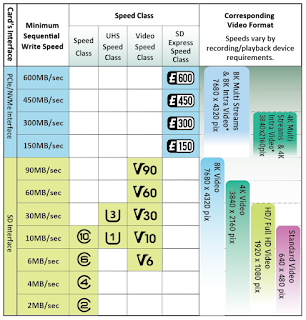
Choosing the right SD or microSD card depends on your device's compatibility with the SD card format (SD, SDHC, SDXC, SDUC) and speed class (UHS, Video Speed Class, SD Express Speed Class).
Summary
Selecting the right type of external storage depends on a multitude of factors, such as your budget, storage needs, desired speed and durability requirements.
Additionally, cloud storage options are becoming increasingly popular, offering convenient access to your data from anywhere with an internet connection.




Comments
Post a Comment