Wi-Fi
Introduction
Wi-Fi standards are sets of technical specifications that define how wireless devices communicate.
- The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) develops these standards under the designation 802.11.
Generations
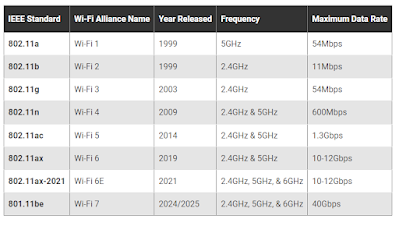
Wi-Fi technology has steadily improved with each generation, offering faster speeds, lower latency and better user experiences across various environments and device types.
- In 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance introduced a user-friendly numbering system for publicly used 802.11 protocols.
- These simplified generational names may appear in device names and product descriptions.
Wi-Fi 5
Wi-Fi 5 is the current mainstream standard, operating in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- The 5 GHz band boasts theoretically faster speeds than the 2.4 GHz band but has a shorter range, especially when penetrating walls, floors and other obstacles.
- This technology significantly improves overall Wi-Fi speed and reduces latency.
Summary
Choosing the best Wi-Fi standard is a personal decision based on your individual needs and budget.
- While newer standards offer faster speeds, an older standard with lower maximum speeds might suffice for your typical internet usage (e.g. browsing, light streaming, etc.)
- Upgrading to newer standards often comes with a higher cost, both for the router and compatible devices.
Ensuring device compatibility and matching the standard to your internet plan's speed are crucial for maximizing benefits.
- To illustrate, it is pointless to invest in a cutting-edge Wi-Fi 6E router if your laptop can only connect to Wi-Fi 4 or your internet plan is only 30 Mbps.
However, investing in newer Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 6E offers several advantages that go beyond just increased speed.
- Future-proofing.
- Improved security with latest protocols like WPA3.
- Better performance in crowded environments, with a new 6 GHz band.
Comments
Post a Comment