Dangerous Drugs Act 1952 and Regulations
Introduction
Apart from Poisons Act 1952 and Regulations, we should also have a fair understanding on Dangerous Drugs Act 1952 and Regulations to be well prepared for Qualifying Examination to Practice Pharmacy.
Today, we are going to have a refresh on legislation requirements in dispensing Dangerous Drugs:
- Dangerous Drugs
- Restriction of Application of Regulations
- Possession
- Control of Import and Export
- Storage
- Prescription
- Keeping of Records
Dangerous Drugs
Dangerous Drugs means any drug or substance which is for the time being comprised in the First Schedule. Some examples are:
- Cannabis
- Amphetamine
- Cocaine*
- Codeine*
- Dihydromorphine
- Diphenoxylate*
- Fentanyl
- Heroin
- Hydrocodone
- Hydromorphone
- Ketamine
- Methadone
- Morphine
- Oxycodone
- Oxymorphone
- Pethidine
- Pholcodine*
- Piminodine
- Remifentanil
* All products registered under the Control of Drugs and Cosmetics Regulations 1984 will be a Group C Poison under Poisons Act 1952.
Restriction of Application of Regulations
Regulation 25 - Nothing in these Regulations, except Paragraph (8) of Regulation 15 and Regulation 16 of these Regulations, shall apply to a product containing any drug specified in the Third Schedule.
- The products in no. 1 of the Third Schedule will be regulated as dispensed medicines under Poisons Act 1952 and Regulations.
- The products in no. 2 of the Third Schedule will be regulated under Poisons (Psychotropic Substance) Regulations 1989.
- Hence, morphine powder is regulated under Dangerous Drugs Act 1952 and Regulations, but morphine sulphate 10 mg tablet is regulated under Poisons (Psychotropic Substances) Regulations 1989.
Possession
Under Regulation 6, a person shall not be in possession of a drug or preparation unless it is lawfully supplied by a registered medical practitioner/veterinary surgeon or on a prescription.
Under Regulation 7, the supplier (either a qualified medical practitioner or licensed pharmacist), shall not deliver it to a person who purports to be sent by or on behalf of the recipient, unless that person either:
- Is a person authorized under these Regulations to be possession of that drug or preparation; or
- Produces to the supplier a statement in writing signed by the recipient to the effect that he is authorized by the recipient to receive the drug or preparation in question on behalf of the recipient and the supplier is reasonably satisfied that the document is a genuine document.
Control of Import and Export
Under Section 4 and Section 5, no person shall import to Malaysia or export from Malaysia any raw opium, coca leaves, poppy-straw or cannabis except under and in accordance with the authorization of the Minister.
Refer Section 19 and Section 20 for export and import of dangerous drug respectively
- “Export authorization” means an authorization issued by a competent authority in a country from which a dangerous drug is exported;
- “Import authorization” means a licence, issued by a competent authority in a country into which it is intended to import dangerous drugs.
Storage
As stated in Regulation 9(2) of Dangerous Drugs Regulations 1952, every drug or preparation shall be kept in a locked receptacle which can only be opened by authorized registered pharmacist or some assistant of his being a registered pharmacist.
Prescription
- be in writing and signed by the registered medical practitioner/dentist/veterinary surgeon giving it with his usual signature and dated by him;
- specify the address of the registered medical practitioner/dentist/veterinary surgeon giving it
- specify the name and address of the person for whose treatment it is given or, if it is given by a veterinary surgeon, of the person to whom the article prescribed is to be delivered;
- have written thereon, if given by a dentist, the words "for local dental treatment only", and if given by a veterinary surgeon, the words "for animal treatment only"; and
- specify, if prescribes a preparation containing or compounded of preparations all of which are contained in the British Pharmacopoeia or the British Pharmaceutical Codex, the total amount of the preparation or of the each preparation, as the case may be, and in any other case the total amount of the drug to be supplied.
Regulation 12 states that the person dispensing a prescription shall, at the time of dispensing it,
- Mark thereon the date on which it is dispensed and in the case of a prescription which may be dispensed a second or third time, the date of each occasion on which it is dispensed, and
- Shall retain it and keep it on the premises where it is dispensed and so as to be all times available for inspection.
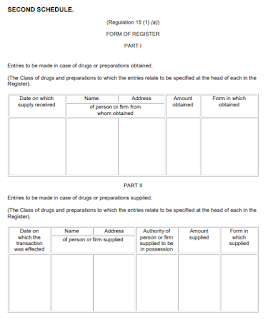
Keeping of Records
- A Register in the form that set out in the Second Schedule, in the national language or in English
- A separate Register or a separate part of the Register with respect to each of the drugs
- The required entry must be made on the day in which the drug or preparation is received by or supplied by him, or, if that is not reasonably practicable, on the day next following the said day
- No cancellation, obliteration shall be made of an entry in the Register and any correction of an entry must be made by way of a marginal note or a footnote which must be specify the date on which the correction is made
For the purpose of this Regulation, "a proper reference" means a reference which is entered in the Register under the same date as that on which the entry in the day-book or in the Prescription Book was made and is otherwise such as to enable that entry to be easily identified.
Under Regulation 16, all registers, records, book, prescriptions, signed orders and other documents shall be kept for a period of 2 years from the data on which the last entry is made.

Hi, regarding the restriction of application of regulations (Items 1 and 2 of the Third Schedule), do these restrictions apply only to oral preparations, or do they also cover injections? For example, are pethidine injection and morphine injection regulated as psychotropic substances or dangerous drugs (DD)? Thank you very much for your help.
ReplyDeletePethidine injection and morphine injection should be regulated as psychotropic substances since they are commercial products.
Delete