Earwax (Cerumen) Impaction
Introduction
Earwax (Cerumen) is a naturally occurring substance that cleans, protects and lubricates the auditory canal.
A cerumen impaction is an accumulation of cerumen that causes symptoms such as hearing loss, ear discomfort (to variable degrees) and a sensation that the ear is blocked.
- Rarely, it can cause dizziness and nausea.
NOTE: Young children, elderly, individuals with a cognitive impairment and hearing-aid users are at increased risk of cerumen impactions.
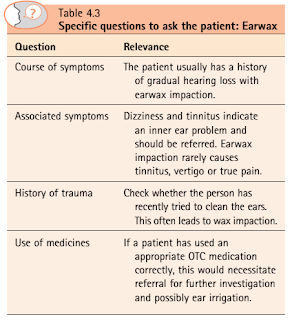
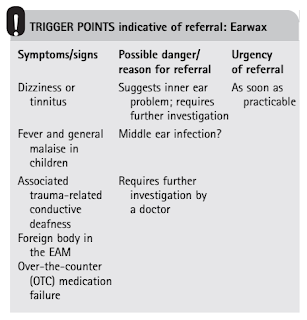
Questions to Ask
Management
Cerumenolytics have been used for many years to help soften, dislodge and remove impacted earwax.
- Ideally, the ear should be examined prior to treatment.
A Cochrane Review identified 10 studies with a total of 623 participants (900 ears) that examined oil-based treatments (e.g. triethanolamine polypeptide, almond oil, benzocaine, chlorobutanol) and water-based treatments (e.g. docusate sodium, carbamide peroxide, phenazone, choline salicylate, urea peroxide, potassium carbonate) and other active comparators (e.g. saline or water alone). They compared these treatments with each other and to no treatment.
- The authors found only 1 study that showed a significant increase in the proportion of patients with complete clearance of earwax (22%) compared with placebo (5%).
- However, comparisons of active treatments with water or saline, or with each other, failed to demonstrate any significant differences. In other words, no apparent difference in cerumenolytic agents.
- Hence, these agents should not be used in patients with a tympanic membrane perforation.
Advice to Patients
Ears are largely self-cleaning. Cotton wool buds should never be poked into the ear to clean or clear it as wax is pushed further in and it is possible to damage the eardrum.
Do not use ear candling which is ineffective and has a risk of serious injuries.
Comments
Post a Comment