Haemorrhoids
Introduction
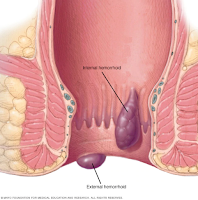
Haemorrhoids, also called piles, are swollen veins develop inside the rectum (internal haemorrhoids) or under the skin around the anus (external haemorrhoids).
- Haemorrhoids can occur at any age but are rare in children and adults younger than 20 years.
- There is a high incidence of haemorrhoids in pregnant women.
Symptoms
Symptoms experienced by the patient are dependent on the severity or type of haemorrhoid.
- Bright red painless rectal bleeding is the most common symptoms.
- Blood is usually seen as spotting around the toilet, streaking on toilet tissue or visible on the surface of the stool.
- Internal haemorrhoids are rarely painful, whereas external haemorrhoids can cause pain due to the cushion becoming thrombosed.
- Pain is not always present. If it is, the pain is described as a dull ache that increases in severity when the patient defecates, leading to patients ignoring the urge to defecate. This can then lead to constipation, which in turn will lead to more difficulty in passing stools and further increase the pain associated with the defecation. NOTE: A severe sharp pain on defecation may indicate anal fissure.
- Itching and irritation are also commonly observed.
- Symptoms are often intermittent, and each episode usually lasts from a few days to few weeks.
Indicative of Referral
Severe (e.g. prolapsing haemorrhoid) or persistent (>3 weeks) cases
- May need surgical intervention, such as rubber ligation, sclerotherapy injections and haemorrhoidectomy.
Severe pain associated with defecation
- Anal fissure?
Abdominal pain, abdominal distension or vomiting
- Symptoms of haemorrhoids remain local to the anus. Any of more widespread symptoms suggest other problems and require referral.
Blood mixed in the stool
- Suggests GI bleeds or inflammatory bowel disease.
Management
General measures to prevent constipation will help decrease straining during defecation, ease the symptoms of haemorrhoids and reduce recurrence.
- Eat high-fiber foods, e.g. fruit, vegetables, bran and whole-grain bread
- Drink plenty of fluids
- Exercise
- Consider fiber supplements or laxatives (if needed)
Pharmacological intervention - Most products contain a combination of these agents, e.g. Xyloproct and Proctosedyl.
- Local anaesthetics (e.g. benzocaine, lidocaine, cinchocaine)
- Their action is short-lived (require frequent application) and will produce temporary relief from perianal itching and pain.
- There is a possibility that local anaesthetics may cause sensitisation, and their use is best limited to a maximum of 2 weeks.
- Astringents (e.g. allantoin, bismuth, zinc oxide, Peru balsam)
- Theoretically, they precipitate surface proteins, thus producing a protective coat over the haemorrhoid.
- Topical steroids (e.g. hydrocortisone)
- Steroid have proven effectiveness in reducing inflammation.
- The use of such products is restricted to those over 18 and treatment should not be used continuously for longer than 7 days.
- Topical corticosteroids may exacerbate local infection and cause skin atrophy.
- Flavonoids (e.g. diosmin and hesperidin)
- Dietary supplementation with flavonoids is a common alternative treatment that is popular in continental Europe and the Far East.
- As an adjunct, their use has been shown to reduce acute symptoms and secondary haemorrhage after haemorrhoidectomy.
The itching of haemorrhoids can often be improved by good anal hygiene, since the presence of small amounts of faecal matter can cause itching.
- The perianal area should be washed with warm water as frequently as practicable, ideally after each bowel movement.
- Otherwise, patients should be advised to use soft, unscented toilet paper to wipe the perianal area to avoid soreness after wiping.
Summary
OTC creams and ointments can be used for internal (with the use of an applicator) and external haemorrhoids.
- They should be applied in the morning, at night and after each bowel movement.
On the other hand, suppositories are recommended for internal haemorrhoids.
- Insertion is easier if the patient is crouching or lying down.
External Links
- Comparative efficacy and tolerability of two ointment and suppository preparations ('Uniroid' and 'Proctosedyl') in the treatment of second degree haemorrhoids in general practice, 1988
- Fiber for the treatment of haemorrhoids complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis, 2006
- Meta-analysis of flavonoids for the treatment of haemorrhoids, 2006
- Counselling Patients With Haemorrhoids, 2011
Good
ReplyDeleteHemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen blood vessels located in the rectum or anus. They can be caused by various factors, including straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation or diarrhea, pregnancy, and obesity. Hemorrhoids can be painful and may lead to symptoms such as bleeding, itching, and discomfort. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, over-the-counter medications, and in severe cases, medical procedures like rubber band ligation or surgical removal. If you're experiencing symptoms of hemorrhoids, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance on treatment.
ReplyDelete