Rectal Route
Introduction
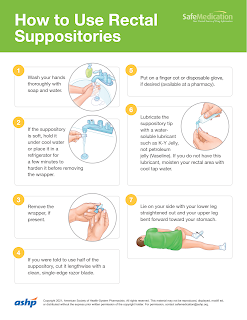
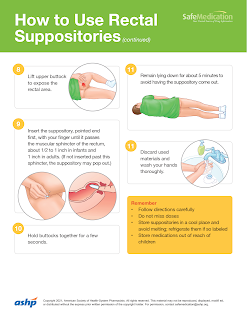
Drugs can be given rectally in solution, suppository or emulsion form.
Indications
This route of drug administration is
- Generally for local effect rather than systemic effects.
- Such as constipation, anal fissures and haemorrhoids.
- Indicated for drugs inactivated by the gastrointestinal fluids or liver when given orally [bypassing first-past (presystemic) metabolism]
- Indicated when the oral route is precluded, for example when a patient is vomiting or unconscious (i.e. when the patient is unable to swallow).
Disadvantages
- The rectal route is inconvenient.
- Can affect patient compliance especially for chronic ailments because of privacy and cultural aspects.
- Drug absorption is often irregular and difficult to predict.
- It depends on the positioning of the dosage form in the rectal cavity and on interpatient variations in rectal content.
Comments
Post a Comment