Chickenpox
Introduction
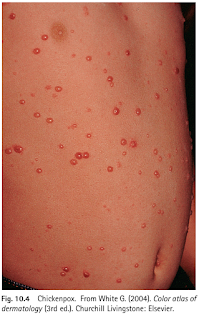
Chickenpox is a highly contagious illness caused by primary infection with the varicella zoster virus, characterized by vesicular rash and fever.
- It is contagious from a few days before the onset of rash until all lesions have crusted over.
- Main route of transmission is through contact with infected persons via
- Inhalation of respiratory droplets and aerosols generated by skin lesions.
- Direct contact with droplets of vesicular fluid from skin lesions.
Reinfection results in people suffering from shingles.
Symptoms
The incubation period is typically 2-3 weeks.
- Before the rash develops, the patient might experience up to 3 days of prodromal symptoms that could include fever, headache and sore throat.
The rash typically begins on the face, stomach, and back before spreading to other parts of the body.
- Initially, lesions appear as small red lumps that rapidly develop into vesicles, which curst over after 3-5 days.
- New lesions form for up to 1 week with the total number of vesicles usually 250-500, though may range from 10 to >1000 vesicles.
- The vesicles are often extremely itchy, and secondary bacterial infection due to the vesicles being scratched is not unusual.
NOTE: Chickenpox typically presents in children. In infants, adults and immunocompromised patients, symptoms may be more severe.
Management
In otherwise healthy children ≤12 years old, disease is usually self-limiting.
Treatment is symptom-directed and antiviral medication is usually not needed.
- Paracetamol may ease fever, headaches, aches and pains.
- Soothing creams (e.g. calamine lotion) and oral antihistamines to relieve pruritus.
- Fluid and electrolytes to maintain hydration.
Give antiviral medication (e.g. acyclovir) for immunocompromised patients, patients with chronic skin or lung disease, severe cases of varicella, neonatal varicella, adults, and pregnant women.
NOTE: Ibuprofen and other NSAIDs should be avoided in children and adults with chickenpox as this is associated with an increased risk of skin infection.
Prevention
Varicella virus vaccine is recommended to prevent chickenpox in adults and children ≥12 months old, unless immunocompromised.
Use varicella zoster immune globulin (VariZIG) as postexposure prophylaxis in immunocompromised patients, pregnant women, premature infants, and neonates born to mothers with evidence of infection if able to give within 96 hours of exposure to varicella (preferably within 48 hours).
Summary
Children with chickenpox should be kept away from school or nursery until no more crops appear and all the spots have crusted over (which takes about 5 days after the onset of rash).
- In the meantime, having contact with immunocompromised people, pregnant women and babies aged 4 weeks or less should also be avoided.
External Links
- CDC - Chickenpox (Varicella)
- DermNet - Chickenpox
- Don't forget how severe varicella can be--complications of varicella in children in a defined Polish population, 2013
- Global Varicella Vaccine Effectiveness: A Meta-analysis, 2016
- Effectiveness, immunogenicity and safety of one vs. two-dose varicella vaccination:a meta-analysis, 2018
- Protection against varicella with two doses of combined measles-mumps-rubella-varicella vaccine or one dose of monovalent varicella vaccine: 10-year follow-up of a phase 3 multicentre, observer-blind, randomised, controlled trial, 2019
Comments
Post a Comment