Tablet Excipients
Introduction
Whenever customers/patients were introduced with generic drugs, their first concern will be "are they exactly the same as the innovator brand product?".
- Technically, both innovator brand and generic brand products contain the same quantity of active pharmaceutical ingredients (the substance that we believe to give the therapeutic benefit), but may contain different pharmaceutical excipients, especially preservatives and colourants.
Functions
Pharmaceutical excipients are basically everything other than the active pharmaceutical ingredient. Depending on the intended main function, the excipients used in tablets are subcategorized into different groups. However, many substances used in tablet formulation can be multifunctional.
Antiadherent
- Antiadherents prevent sticking to punches and die walls.
- Binders or adhesives are the substances that promote cohesiveness. It is added to a drug-filler mixture to ensure that granules and tablets can be formed with the required mechanical strength.
Buffer
- Buffers are added to maintain a required pH since a change in pH may cause significant alteration in stability.
Colourant
- Colourants are added to tablets to aid identification and increase stability of light-sensitive drugs.
- Often useful to match colour with flavour to improve the attractiveness of the product.
Coating
- Tablet coatings protect tablet ingredients from deterioration by moisture in the air and make large or unpleasant-tasting tablets easier to swallow.
Disintegrants
- A disintegrant is included in the formulation to ensure that the tablet, when in contact with a liquid, breaks up into small fragments (increase surface area), which promotes rapid drug dissolution.
Filler (or diluent)
- To form tablets of a size suitable for handling, a lower limit in terms of powder volume and weight is required. Therefore, a low dose of a potent drug requires the incorporation of filler into the formulation to increase the bulk volume of the powder and hence the size of the tablet.
Flavour
- Flavouring agents are incorporated into a formulation to give the tablet a more pleasant taste or to mask an unpleasant one.
Glidants
- Glidants are added to the formulation to improve the flow properties of the material which is to be fed into the die cavity and aid in particle rearrangement within the die during the early stages of compression.
Lubricant
- The function of the lubricant is to ensure that tablet formation and ejection can occur with low friction between the solid and the die wall.
Preservative
- To control the microbial bioburden of the formulation.
Sorbent
- Sorbents are substances that are capable of sorbing some quantities of fluids in an apparently dry state. Thus, oils or oil-drug solutions can be incorporated into a powder mixture which is granulated and compacted into tablets.
Sweetener
- Especially used in the chewable, dispersible, sublingual tablet
Important Things
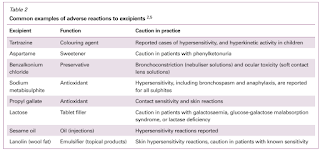
Ideally, pharmaceutical excipients should be inert and safe (no acute or chronic toxicity).
However, in reality, they can cause adverse and hypersensitivity reactions in patients.
Plus, studies have shown that some excipients can have a significant effect on the performance of an oral solid dosage form, including bioavailability and stability.
Also, patients may ask to avoid excipients of animal origin for personal or religious reasons.
- For example, some vegans request medicines that do not contain gelatin, and Jehovah’s Witnesses may seek to avoid products containing albumin from a human source.
Comments
Post a Comment