Physical Examination
Introduction
The complete health assessment of an individual has 3 major components.
- The interview and health history
- i.e. the source of subjective information
- The general survey and measurement of vital signs
- Physical examination
Method of Assessment
Physical examination is the evaluation of objective anatomic findings gathered through 4 distinct activities, which are done in the stated order.
- Inspection
- Palpation
- Percussion
- Auscultation
The definitive purpose of the physical examination is to identify first the "normal" state and then any variations from that state through validation of the patient's complaints and symptoms, screening of the patient’s general well-being or deteriorating status, and monitoring of the patient's current health problems.
Inspection
Inspection involves the use of vision, hearing and smell to examine patients or the specific area that is being assessed.
Palpation
Palpation uses the hands to feel for abnormalities on the surface or deeper if required. One should start with light palpation and move deeper as needed.
- To feel the size of internal organs
- To feel for tenderness
- To measure a pulse
- Assess peripheral oedema
- Feel of palpable lymph nodes
Percussion
Percussion involves lightly striking the body surface with the purpose of producing a sound.
- A structure housing more air (e.g., the lungs) produces a louder, lower, longer sound than a denser, more solid structure (e.g., the thigh muscle), which produces a softer, higher, shorter sound. The density of a thick tissue or mass absorbs the sound and blunts the tone.
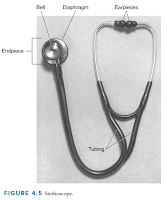
Auscultation
Auscultation is the act of listening to the sounds created in the lungs, heart, blood vessels and abdominal viscera, usually using a stethoscope.
- The wide range of normal sounds must be adequately learned before abnormal and extra sounds can be distinguished.
Summary
Typically, pharmacists do not perform a complete physical examination, but it is important for us to understand the principles and methods.
Comments
Post a Comment