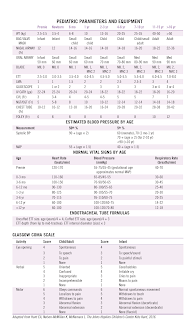
Vital Signs
Introduction
Vital signs are measurements of the body's most basic functions, hence providing valuable information concerning a patient's general state of health.
- Any abnormal values require further investigation and recheck.
The 4 main vital signs routinely monitored by health care professionals are:
- Body temperature (BT)
- Pulse rate (PR)
- Respiration rate (RR)
- Blood pressure (BP)
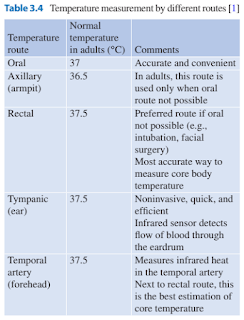
Body Temperature
To maintain normal metabolic function, the core temperature of the body is regulated by hypothalamus to stay within a very narrow range.
- Heat production, which occurs primarily through metabolism and exercise, is balanced with heat loss, which occurs mainly through evaporation of sweat.
- The normal body temperature of a person varies depending on age, gender, recent activity, food and fluid composition, time of day, and in women, the stage of the menstrual cycle.
Temperature can be measured by a variety of thermometer by a variety of routes.
- Rectal and tympanic membrane temperatures tend on average to be higher than oral temperature while axillary temperatures are lower.
- An oral temperature greater than 38C is considered fever.
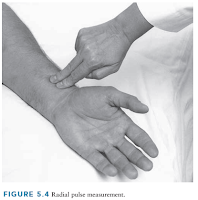
Pulse Rate
The normal range used in the adult is between 60 to 100 beats per minute with rates over 100 beats per minute and rates below 60 beats per minute, referred to as tachycardia and bradycardia respectively. The pulse rate may fluctuate and increase with exercise, illness, injury and emotions (e.g. anxiety).
- Athletes, such as runners, may have a resting heart rate <50-60 bpm due to cardiovascular adaptation from exercise.
- For a patient who is on beta-blocker, bradycardia (HR <60 bpm) may warrant dose reduction, depending on if they are symptomatic, how low their HR is and the indication of beta-blocker therapy.
Respiratory Rate
Inspection is used to evaluate the patient's respiratory rate (the rising of a patient's chest signify a breath).
- Since a person's breathing may be altered if they become aware of it, it is best not to tell the patient when assessing their respiratory rate.
The normal breathing rate is about 12 to 20 breathes per minute in an average adult.
- It may increase with fever, illness and other medical conditions (e.g. asthma exacerbation, acute exacerbation of COPD or pneumonia).
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force of the blood pushing against the artery walls during contraction and relaxation of the heart. It depends on cardiac output, the volume of blood ejected by the ventricles per minute and the peripheral vascular resistance.
- Systolic BP - the maximum pressure that is felt on the arteries during left ventricular contraction.
- Diastolic BP - the resting pressure that the blood exerts between each ventricular contraction.
Factors affecting blood pressure include age, race, diurnal rhythm, weight, exercise and emotions.
Refer to this post for more info on blood pressure monitoring.
Comments
Post a Comment