Renal Replacement Therapy
Introduction
End-stage renal disease (ESRD) is a common term used for patients in CKD stage 5 (GFR <15 ml/minute/1.72m2). These patients may require renal replacement therapy such as
- Dialysis
- Renal transplant
Dialysis
The principle of dialysis is simple. The patient's blood and a dialysis solution are positioned on opposing sides of a semi-permeable membrane across which exchange of metabolites occurs.
The 2 primary types of dialysis are haemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD).
- Neither has been shown to be superior to the other in any particular patient group.
- The choice of dialysis mode is made based on the patients' concomitant diseases, preferences and socioeconomic factors.
Factors Affecting Drug Removal During Dialysis
When a patient receives dialysis, the pharmacist must consider the amount of medication cleared during dialysis in order to recommend the correct dose and interval.
- Medications that are removed during dialysis must be given after dialysis or may require a supplemental dose following dialysis.
Factors affecting drug removal during dialysis
- Drug characteristic
- Molecular size - Smaller molecules are more readily removed.
- Volume of distribution - Drugs with a large Vd are less likely to be removed.
- Protein-binding - Highly protein-bound drugs are less likely to be removed.
- Dialysis factors
- Membrane - High-flux (large pore size) and high-efficiency (large surface area) HD filters removes more substances than conventional/low-flux filters.
- Blood flow rate - Higher dialysis blood flow rates increase drug removal over a given time interval.
Renal Transplantation
One of the major challenges for renal transplantation is identification of a sufficient number of donor kidneys to fulfil demand.
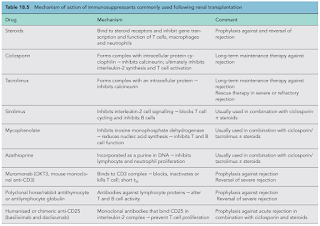
Immunosuppressive drugs are used to control the response as the immune system of the recipient mount against the donor kidney (i.e. alloimmunity).
- Due to their relative non-specificity, the patients are exposed to an increased risk of malignancy and infection, which is an important cause of morbidity and mortality.
Comments
Post a Comment