Extemporaneous Formulation
Introduction
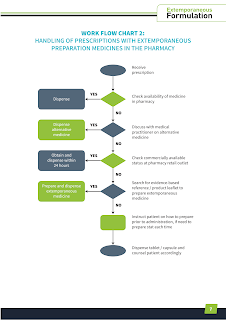
Despite the shifting of pharmacy focus to pharmaceutical care, the practice of compounding pharmaceutical formulations remains an essential skill for pharmacists. Being a drug expert, we are expected to know them all.
- In the 1920s, hiring a hospital pharmacist in the United States was necessary for controlling the inventory and manufacturing alcohol-containing preparations, which were expensive to obtain commercially.
- Nowadays, it is recommended to use commercially available products whenever possible. If no suitable commercial product exists and no therapeutic alternative, then extemporaneous preparations should be made based on evidence-based references.
- When no stability information is available, pharmacist may dispense oral tablet or capsule and direct the caregiver to freshly prepare just prior to administration.
Extemporaneous Formulation References
There are many references available for extemporaneous formulation, including
- Australian Pharmaceutical Formulary and Handbook, 2024
- British Pharmacopoeia
- Extemporaneous Formulations for Paediatric, Geriatric and Special Needs Patients, 2021
- Extemporaneous Ophthalmic Preparations, 2020
- extemp.ie - Ireland
- Gateway Paediatric Pharmacy Group Formulary of Extemporaneous Oral Liquid Medications, 2018 - Southern Illinois University-Edwardsville
- Micromedex NeoFax - Under "Special Considerations/Preparation"
- IWK Compounding Formulas
- Lexicomp - Under "Extemporaneously Prepared"
- Michigan Paediatric Safety Collaboration Standardize Compounded Oral Liquids
- Nationwide Children's Hospital Compounding Formulas
- Pharmaceutical Compounding and Dispensing, 2010
- Pharmaceutical Society of New Zealand Compounded Oral Liquid Formulae
- The International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding
- The International Pharmacopoeia, 2025
- Trissel's Stability of Compounded Formulations, 2018
- United States Pharmacopoeia -National Formulary
There are many references available for extemporaneous formulation, including
- Australian Pharmaceutical Formulary and Handbook, 2024
- British Pharmacopoeia
- Extemporaneous Formulations for Paediatric, Geriatric and Special Needs Patients, 2021
- Extemporaneous Ophthalmic Preparations, 2020
- extemp.ie - Ireland
- Gateway Paediatric Pharmacy Group Formulary of Extemporaneous Oral Liquid Medications, 2018 - Southern Illinois University-Edwardsville
- Micromedex NeoFax - Under "Special Considerations/Preparation"
- IWK Compounding Formulas
- Lexicomp - Under "Extemporaneously Prepared"
- Michigan Paediatric Safety Collaboration Standardize Compounded Oral Liquids
- Nationwide Children's Hospital Compounding Formulas
- Pharmaceutical Compounding and Dispensing, 2010
- Pharmaceutical Society of New Zealand Compounded Oral Liquid Formulae
- The International Journal of Pharmaceutical Compounding
- The International Pharmacopoeia, 2025
- Trissel's Stability of Compounded Formulations, 2018
- United States Pharmacopoeia -National Formulary
Malaysia
Ministry of Health Malaysia has made efforts to search for substantiated references in producing the Extemporaneous Formulation, 2015.
- It standardizes Malaysia MOH facilities' extemporaneous formulation, hence preventing medicine dosing errors occurring due to mix-ups if different strengths are prepared by different pharmacies.
Key Reminders
- When a commercial preparation is available, consider it first.
- As highlighted in policy, stability stated in this manual is applicable to shelf storage in the pharmacy without opening. Once opened, the stability of the preparation should be no longer than 30 days. Maximum quantity of the extemporaneous preparations to be dispensed should not exceed 1 month. Many stability studies do not assess the effect of in-use conditions on physical, chemical and microbiological stability.
- Pharmacy personnel are reminded not to empirically change flavourings or suspending agents because they can affect the pH and stability of the product and result in an unstable product.
- Product should be labelled clearly and stored as recommended within the formula.
- For solution or suspension products, emphasise on the importance of thorough shaking before use.
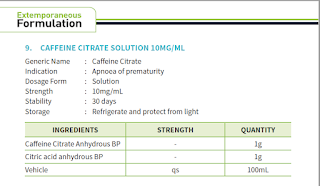
There is a formula that I would like to raise the issue on, that is caffeine citrate solution 10 mg/ml.
Most hospitals in Malaysia are unable to obtain the raw material caffeine citrate anhydrous BP stated. On the other hand, we bought caffeine anhydrous powder instead via import permit. In conversion, 2 mg caffeine citrate = 1 mg caffeine anhydrous. By using caffeine anhydrous powder 1g for 100 ml, the final preparation is actually caffeine anhydrous 10 mg/ml, NOT caffeine citrate 10 mg/ml effectively. This will in turn affects the dosing that we are going to use.
The extemporaneous formula that I personally suggested to use is stated in Micromedex NeoFax:
- Alternatively, an oral solution may be prepared by dissolving 2.5 g of caffeine anhydrous powder in 250 ml of water, yielding a final concentration of 10 mg/ml caffeine base. Solution is stable for 4 weeks refrigerated. Crystals form when stored at low temperature but dissolve at room temperature without loss of potency. Do not freeze.
- In this case, it is important to shake the suspension very well until now visible powder (including before each use) and to use caffeine anhydrous based dosing.
Apart from this reference, another equally important reference in MOH facilities would certainly be X-Temp Master Formulation Sheets.
Vehicle in Extemporaneous Formulation
Flipping through Extemporaneous Formulation, 2015, you may come across a total of 4 common vehicles, namely:
Simple Syrup
- Is a sucrose solution, which has a sweet taste.
- Technically, one or more antimicrobial preservatives may be added.
- Ora-Sweet is the modern version of simple syrup flavoured with a citrus-berry blend for a highly palatable taste. It may be used alone or in combination with other agents. It will retain its flavouring properties when diluted up to 50% with water or suspending agents.
- Ora-Plus is a unique suspending vehicle retains its suspending properties when diluted up to 50% with water, flavouring agents, syrups or alcohol.
- Ora-Sweet and Ora-Plus can be combined in a 50:50 ratio to produce a pleasant tasting elegant suspension.
- Ora-Blend is a flavoured oral suspending vehicle used to simplify the process involved in the extemporaneous compounding of oral suspensions. It combines the suspending properties of Ora-Plus with the flavouring agents of Ora-Sweet. Medicated powder can be incorporated into Ora-Blend to form elegant, uniform and physically stable suspensions.
- It is generally considered acceptable to substitute sugar-containing Ora products with sugar-free Ora products.
- However, it is not advisable to use sugar-containing Ora products if a study has been performed using sugar-free products. This is because sugar can cause chemical stability problems or discolouration with some drugs (e.g. the Maillard reaction).
- Nonetheless, using Ora SF products instead of Ora Sweet may cause physical instability with some specific formulations.
- Orange flavoured, sweetened, sugar-free vehicle.
- Contains specialized suspending system formulated to assist in extemporaneous preparation of oral liquid, non-soluble (suspended), aqueous dosage forms.
- Contains suitable preservatives: Methyl hydroxybenzoate, propyl hydroxybenzoate, potassium sorbate.
- The X-temp Master Formulation Sheets lists many extemporaneous formulations that based on studies using Ora-Sweet/Ora-Plus 1:1 combination. Few local stability studies that have been carried out for X-Temp Oral Suspension include spironolactone 1.25 mg/ml and 5 mg/ml, folic acid 1 mg/ml, captopril 1.25 mg/ml, morphine 10 mg/5 ml, phenobarbitone 10 mg/ml, isoniazid 10 mg/ml, chloral hydrate 40 mg/ml and hydrochlorothiazide 5 mg/ml.
NOTE: X-Temp Oral Suspension and Ora-Blend SF (SF stands for sugar free) are not exactly the same. 2 major differences include:
- Ora-Blend SF has simethicone as an antifoaming agent (not present in X-Temp Oral Suspension).
- Although both Ora-Blend SF and X-Temp Oral Suspension are buffered to a pH of about 4.2, the osmolarity of Ora-Blend SF is slightly higher (1073 mOsm/kg vs 950 mOsm/kg).
Alcohol in Compounding
In pharmaceutical preparations, alcohol is a very important and commonly used solvent.
- In external preparations, it exhibits bacteriostatic property at low concentrations but has bactericidal activity at higher concentrations.
- Coupled with its rapid evaporation property, it is commonly used in production of lotions for external application.
On the other hand, the use of alcohol in internal preparations is generally limited for several reasons.
- Liquid medicines are often given to young children, so the use of alcohol in such preparations may be inappropriate.
- Moreover, some patients of certain faiths (e.g. Muslims) may find alcohol-containing medicines unacceptable.
If ethanol 96% is needed in an internal preparation, it is important to realize that only undenatured ethanol 96% is suitable for internal use due to the toxicity of methanol (methyl alcohol) with denatured ethanol.
- To illustrate, Industrial Methylated Spirits (IMS) is an ethanol that has been "denatured" by the addition of wood naphtha, rendering its unfit for internal use.

Any comment on an economical way to compound clobazam? dosage is 7.5mg bd. Hospital keeps suggesting to quarter the tablet but it breaks so easily. I need a cheap suspending agent. Your help will be most grateful.
ReplyDeleteHave you tried cutting the tablet using a pill cutter that you can buy from community pharmacy?
DeleteYes but I've tried to quarter a 10 mg tablet with multiple types of tablet cutters but they crumble so easily. So is there a suspending agent I can buy locally from a pharmacy here easily available?
DeleteAs far as I know, community pharmacy does not sell suspending agents. However, I highly recommend you to discuss the issue with the pharmacy supplying medication, if possible for them to make extemporaneous preparation or to allow you to freshly prepare suspension for each dosing .
Deletehow about methylcelullose. Do you know where I can purchase the powder?
ReplyDeleteSorry, I do not know. I highly recommend you to speak to your local pharmacist on the issue.
DeleteThe extemporaneous formulations that we practice doing these days mostly have stability studies done (chemical and physical stability).