Probiotics
Introduction
Probiotics is defined as "live microorganisms that, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host."
- Prebiotics - dietary ingredient that is used or fermented by microorganisms (gut flora or probiotic) to yield a beneficial result for human host. Examples include inulin and fructooligosaccharides (FOS).
- Synbiotics - a mixture of prebiotic and probiotic.
Indications
Therapeutic use of probiotics may include:
- Prevention and treatment of diarrhoea
- Treatment of atopic dermatitis - inconsistent evidence
- Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri supplement may reduce crying in infants with colics
- Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in preterm, low-birth weight infants
NOTE: Most studies have been small and use highly variable probiotic preparations, and many have important methodologic limitations, making it difficult to make unequivocal conclusions regarding efficacy.
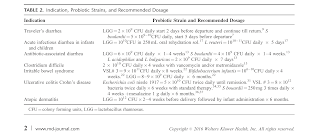
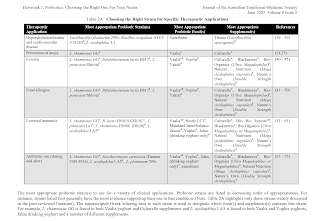
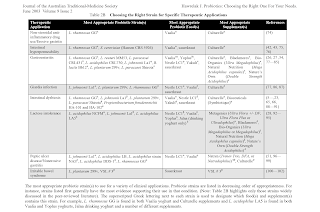
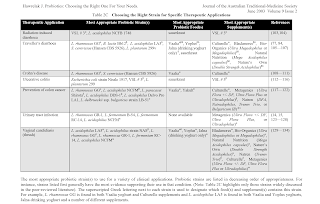
Choosing Probiotics
When searching for the probiotics, pay close attention to
- Colony-forming units (The number of bacteria per dose)
- Types of bacterial strains that are used
- How your probiotics need to be stored and expiration information.
- Which strains and/or brand names have been studied for their effectiveness.
Choosing an Appropriate Probiotic Product for Your Patient: An Evidence-based Practical Guide, 2018
Clinical Uses of Probiotics, 2016
Probiotics: Choosing The Right One For Your Needs, 2003
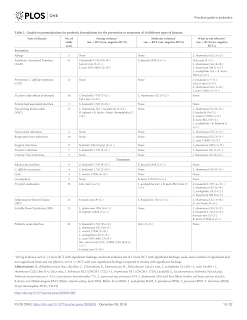
Adverse Effects
Adverse effects related to probiotic use may include

Comments
Post a Comment