Bipolar Disorder
Introduction
Bipolar disorder is characterized by recurrent episodes of elevated or irritable mood and depression, accompanied by changes in sleep and energy and associated with cognitive, physical and behavioural symptoms.
- Bipolar I disorder is characterized by at least 1 episode of mania, and usually episodes of depression and/or hypomania.
- Bipolar II disorder is characterized by a history of major depressive episodes and hypomanic episodes only, without episodes of mania.
Bipolar disorder has a strong genetic basis and a peak onset in young people.
Management
Consider mood stabilizers, such as lithium or valproate, and second-generation antipsychotics (e.g. quetiapine) for the primary treatment of bipolar disorder.
For maintenance monotherapy in patients with bipolar disorder, consider lithium or valproate. If the patient is unable or unwilling to take lithium or valproate, consider lamotrigine or a second-generation antipsychotic.
Consider electroconvulsive therapy for severe manic or depressive episodes.
NOTES:
- Avoid valproate in women of child-bearing potential.
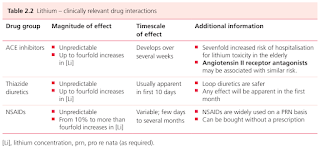
- Because of lithium's relatively narrow therapeutic index, pharmacokinetic interactions with other drugs can precipitate lithium toxicity.
External Links
- The Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry, 2021
- Antidepressants for the acute treatment of bipolar depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis, 2011
- Treatments for acute bipolar depression: meta-analyses of placebo-controlled, monotherapy trials of anticonvulsants, lithium and antipsychotics, 2014
- A network meta-analysis on comparative efficacy and all-cause discontinuation of antimanic treatments in acute bipolar mania, 2015
- Comparative efficacy and tolerability of pharmacological treatments for the treatment of acute bipolar depression: A systematic review and network meta-analysis, 2020
Comments
Post a Comment