Cataract
Introduction
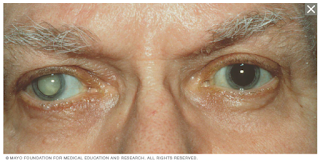
A cataract is a clouding in the lens of the eye, which changes the way light passes through the lens.
- It usually develops slowly and may occur in one or both eyes.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for cataracts include
- Increasing age - the most common cause
- Family history of cataracts
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- Long-term sunlight exposure
- Certain medical conditions, e.g. diabetes
- Certain medicines, e.g. prednisolone
Symptoms
At first, you may not notice that you have a cataract. But over time, cataracts can cause symptoms such as
- Cloudy, blurred or double vision
- Fading or yellowing of colours
- Poor night vision
- Increased sensitivity to glare. A halo may appear around lights
Management
Initially, cataracts may be managed with
- New spectacles,
- Brighter lighting,
- Anti-glare sunglasses and
- Magnifying lenses for reading and other activities.
When cataract symptoms interferes with daily living activities, cataract surgery and placement of an intraocular lens should be considered.
- Once a cataract is removed, it cannot grow back.
- The artificial lens requires no care and can significantly improve vision.
- People who have had cataract surgery may have their vision become hazy again years later. This is usually because the eye's capsule has become cloudy. Ophthalmologists can use a laser to open the cloudy capsule and restore clear vision. This is called a capsulotomy.
Supplements
The role of diet and antioxidant supplements has been studied with mixed conclusions.
- A 2012 Cochrane Systematic Review of nine randomized controlled trials found no evidence to support high doses of vitamin E, vitamin C, or beta-carotene in preventing development or progression of cataract.
- In a 2015 randomized clinical trial, neither selenium nor vitamin E supplementation appear to reduce incidence of age-related cataract in men >50 years old
- A 2019 systematic review about the role of nutrient supplementation on lens pathology found that vitamin C, beta-carotene, and lutein and zeaxanthin had a protective effect against cataract, but this analysis included observational data.
Summary
External Links
- American Academy of Ophthalmology - Cataracts
- MSD Manual Professional - Cataract
- National Eye Institute - Cataracts
- Antioxidant vitamin supplementation for preventing and slowing the progression of age-related cataract, 2012
- Age-related cataract in men in the selenium and vitamin e cancer prevention trial eye endpoints study: a randomized clinical trial, 2015
- The potential role of nutrition on lens pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis, 2019
- Cataract in the Adult Eye Preferred Practice Pattern, 2022
Comments
Post a Comment