Drug-Food Interactions
Introduction
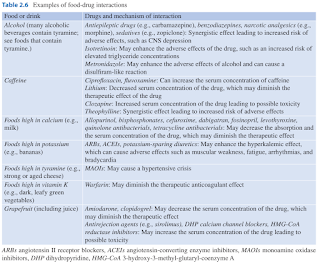
Drug-food interactions
- Are predominantly due to the effect of food on the absorption of the drug (e.g. food and bisphosphonate, antibiotics and iron tablets).
- May refer the list of medications that should be taken before, with or after food for more examples.
- Food can affect the metabolism of drugs by acting as an inducer or inhibitor of enzymes (e.g. grapefruit inhibits CYP3A4).
- Food can also enhance effects or side effects of drugs (e.g. sedation with alcohol) or counteract the effect of drugs (e.g. Vitamin K and warfarin).
NOTE: You may find food interactions in Lexicomp drug monograph.
More Examples
Summary
Different from how we approach drug-drug interactions, we cannot conduct an assessment with drug-food interactions because a patient's complete diet history is incomplete.
- On the other hand, we shall educate patients on potential drug-food interactions to minimize the risk.
Thank you
ReplyDelete