Co-trimoxazole in Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonia
Introduction
Co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim combined with sulfamethoxazole, also known as Bactrim) is used to treat and prevent pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) in people with immunosuppression, such as those with HIV infection.
Mechanism of Action
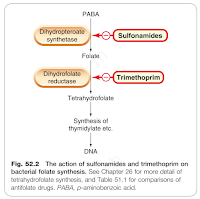
Both trimethoprim and sulfonamides inhibit bacterial folate synthesis, but at a different step in the pathway.
Dosage
Co-trimoxazole comes in both double-strength and single-strength tablets.
- Each double-strength tablet contains trimethoprim 160 mg and sulfamethoxazole 800 mg.
- Each single-strength table contains trimethoprim 80 mg and sulfamethoxazole 400 mg.
NOTE: Weight-based dosing recommendations are based on the trimethoprim component.
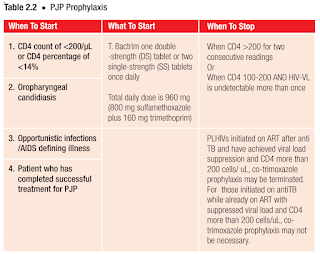
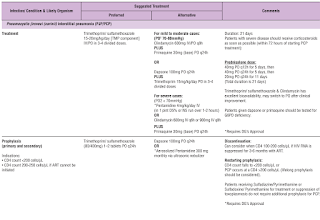
Use in Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia (PJP)
Co-trimoxazole is recommended for pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) prophylaxis to all susceptible individuals as it has been shown to decrease the risk of PJP by 9-fold in this population.
- As an alternative to co-trimoxazole preventive therapy, dapsone at dose of 100 mg daily may be used (G6PD test must be normal prior to initiation).
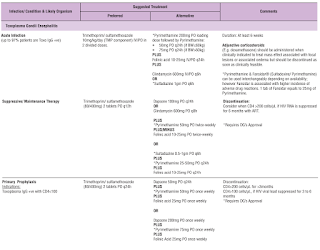
NOTE: Co-trimoxazole is also used off-label for primary prophylaxis of toxoplasma Gondii encephalitis in patients with HIV.
Contraindications
Co-trimoxazole is
- Absolutely contraindicated in severe allergy to sulfa-containing drugs and babies <6 weeks old (due to theoretical increased risk of kernicterus).
- Relatively contraindicated in severe liver disease, severe anaemia due to folate deficiency or severe pancytopenia.
Immediate or delayed hypersensitivity reactions may occur with co-trimoxazole.
- Immediate: Urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis
- Delayed: Maculopapular skin rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Sulfonamides increase the risk of haemolysis in G6PD deficiency.
NOTE: Dosage adjustment is required for renal impairment (CrCl <30 ml/min).
Pregnancy
Co-trimoxazole is recommended for the treatment and prophylaxis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) in pregnant patients with HIV because of the considerable maternal benefits of therapy.
- However, due to the risk of birth defects, supplemental folic acid at high doses (>0.4 mg/day) may be considered during the first trimester only.
- When sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is used during the first trimester, a foetal ultrasound is recommended at 18 to 20 weeks' gestation to evaluate foetal anatomy
Comments
Post a Comment