Oral Anticoagulants
Introduction
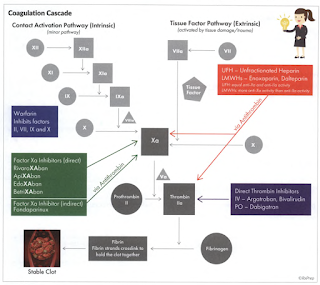
Blood coagulation means the conversion of liquid blood to a clot. The main event is the conversion by thrombin of soluble fibrinogen to insoluble strands of fibrin, the last step in a complex enzyme cascade.
Oral anticoagulants are used mainly for venous thromboembolism (treatment and prevention) and stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation.
- Bleeding is a common and serious complication of anticoagulant therapy.
NOTE: The lack of clinician familiarity with recommended dosing was illustrated in a 2017 report involving over 1500 patients with venous thromboembolism (VTE) who were treated with a DOAC.
Warfarin
Warfarin is a vitamin K antagonist. Vitamin K is required for the carboxylation (activation) of clotting factors II, VII, IX and X.
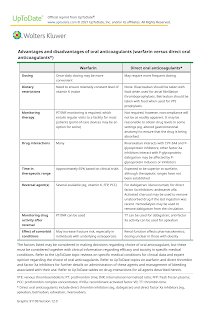
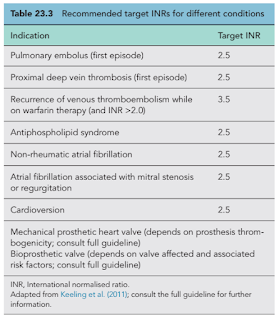
Warfarin has a narrow therapeutic range and requires careful monitoring of the international normalized ratio (INR), which is affected by many drugs and changes in the dietary vitamin K.
Antidote: Vitamin K
Direct Thrombin Inhibitor
Dabigatran (Pradaxa) directly inhibit thrombin (Factor IIa).
Importantly, dabigatran capsules should only be dispensed and stored in the original bottle (with desiccant) or blister package in which they came, due to the potential for product breakdown from moisture and resulting loss of potency.
- Patients should not store or place this agent in any other container, such as pill boxes or pill organizers.
- Once the bottle is opened, the pills inside must be used within four months.
- The capsules should not be crushed or opened before administration, as removal of the capsule shell results in dramatic increases in oral bioavailability
Antidote: Idarucizumab
Factor Xa Inhibitor
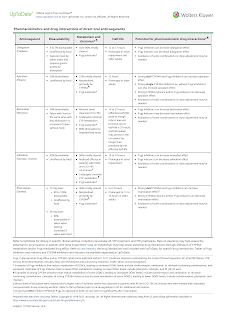
Apixaban (Eliquis), betrixaban (Bevyxxa), edoxaban (Lixiana, Savaysa) and rivaroxaban (Xarelto) work by inhibiting factor Xa directly. These oral gents are taken once or twice daily and require no laboratory monitoring for efficacy.
Antidote for apixaban and rivaroxaban: Andexanet alfa (Andexxa)

Comments
Post a Comment