Erectile Dysfunction
Introduction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) (commonly known as impotence) is the persistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance.
- It can occur at any age, with studies involving men over the age of 40 reporting rates between 19% and 50%.
- Prevalence also increases with increasing age and is due to chronic disease, co-morbid conditions and age-related changes.
Aetiology
Erectile dysfunction tends to have an organic (about 80%) or psychological cause.
- Organic causes broadly fall in to blood flow problems, conditions affecting nerve impulses and hormone regulation or structure abnormalities.
- Psychological causes range from depression to performance anxiety.
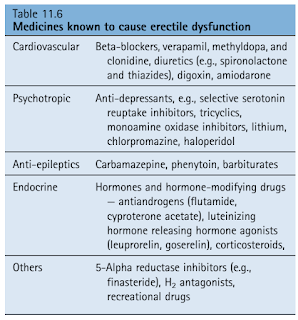
Erectile dysfunction can also be a side-effect of drugs.
Management
Determine and treat underlying cause if possible.
- Erectile dysfunction is often associated with conditions such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia or cardiovascular disease, and may be an indicator for unrecognised disease.
The recommended approach for the erectile dysfunction is a combination of drug treatment and lifestyle changes (including exercise, reduction in body mass index, smoking cessation and reduced alcohol consumption).
- In males with low cardiac risk, erectile dysfunction can be treated using phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, vacuum erection devices, intracavernosal therapy or penile implants.
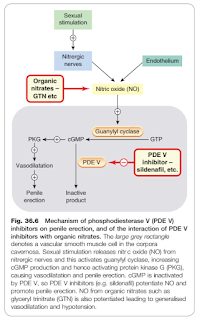
Oral phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, e.g. sildenafil, tadalafil and vardenafil.
- Is the first-line drug treatment, regardless of the cause.
- Onset is about 30 minutes to 1 hour (avanafil may be effective within 15 minutes).
- PDE5 inhibitors do not produce an erection without sexual stimulation and activity.
- Avanafil, sildenafil and vardenafil are short-acting (effective for about 6–8 hours) while tadalafil is long-acting (up to 36 hours).
- The main safety concerns relate to its use in those with recent cardiovascular disease events, such as myocardial infarction, unstable angina or stroke, and its use at the same time as nitrate drugs for angina is contraindicated due to a risk of fatal hypotension.
- If a nitrate is required after a PDE5 inhibitor has been taken, wait at least 24 hours with sildenafil or vardenafil, 12 hours with avanafil and 48 hours with tadalafil before giving the nitrate. A longer period may be required if elimination of the PDE5 inhibitor is delayed (e.g. due to drug interaction, renal or hepatic impairment). Monitor response carefully.
- Vision loss due to non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy (NAION) has been reported; cases include patients treated for pulmonary hypertension, some of whom were female. An observational study suggests an approximate 2‑fold increase in risk of acute onset of NAION after recent use of PDE5 inhibitors.
- Treatment with drugs that can cause hypotension, particularly selective alpha-blockers, may add to hypotension caused by PDE5 inhibitors. If using with an alpha-blocker, stabilise alpha-blocker therapy before starting the PDE5 inhibitor, use the lowest starting dose of the PDE5 inhibitor and, if using prazosin, consider separating doses by at least 4 hours (6 hours with vardenafil).
- Although headache is common for all these drugs; that caused by tadalafil lasts for 3-8 hours. Sildenafil appears most likely to cause visual changes and tadalafil to cause back or muscle pain. Vardenafil has prolonged the QT interval in healthy volunteers.
NOTE: There is concern that symptomatic treatment may lead to curable or serious diseases not being investigated.
Herbal Remedies
Based on a 2021 systematic review, Panax ginseng, Pygnogenol, Prelox and Tribulus terrestris have promising evidence as herbal products, alongside L-arginine as a nutritional supplement, for ED based on IIEF outcomes, and warrant further clinical investigation.
External Links
- Mayo Clinic - Erectile dysfunction
- Mayo Clinic - Dietary supplements for erectile dysfunction: A natural treatment for ED?
- NHS UK - Erectile dysfunction (impotence)
- 'All Natural' Alternatives for Erectile Dysfunction: A Risky Proposition, 2015
- Efficacy of Tongkat Ali (Eurycoma longifolia) on erectile function improvement: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, 2015
- Alternative medicine and herbal remedies in the treatment of erectile dysfunction: A systematic review, 2021
- Proton Pump Inhibitors: Risk of Erectile Dysfunction, 2024

hello
ReplyDeleteSeveral common medical conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease can impair blood flow or nerve function, leading to erectile dysfunction. Managing these underlying health issues is key to improving sexual performance and overall well-being.
ReplyDelete