Ingredients in Skin Care
Introduction
The skincare market is overflowing with products, making informed choices a daunting task.
- To navigate this abundance, understanding the key ingredients listed on product label is crucial.
By law, companies list ingredients in descending order of concentration, allowing you to see how much (or how little) of a key ingredient is actually present.
- "Aqua" simply translates to water, a common filler ingredient.
Here are some resources for researching cosmetic ingredients.
Alpha-hydroxy Acids (AHA)
Alpha-hydroxy acids (e.g. glycolic, lactic, mandelic and citric acids) are chemical exfoliants that gently remove dead skin cells, revealing a brighter, smoother complexion.
- Besides exfoliation, they may be used for pH adjustment in cosmetics.
- Also, lactic acid have been shown to promote ceramide biosynthesis, and further improve skin dryness, scaling and transepidermal water loss
Possible side effects include mild irritation and increased photosensitivity.
Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs)
Salicylic acid penetrates deeper into pores to clear out oil and dead skin cells, making it ideal for acne-prone skin.
- Concentrations between 2-6% are used for dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, ichthyosis, psoriasis; while higher concentrations (up to 70%) are used to remove warts, corns and calluses
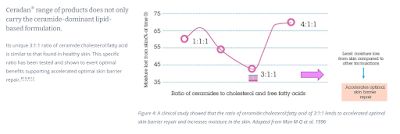
Ceramides
These naturally occurring lipids play a vital role in both water retention and barrier function within the stratum corneum (outermost skin layer).
- Eczema-prone skin has reduced levels of lipids, particularly ceramide, compared to healthy skin, leading to increased moisture loss from the skin and skin dryness.
Dimethicone
Dimethicone, a silicone-based polymer, is frequently used as an emollient and a skin protectant (against water-soluble irritants) in skincare products.
- Creams, lotions, and ointments containing dimeticone are used for the prevention of bedsores and napkin rash and to protect the skin against trauma due to incontinence or stoma discharge.
- Silicones are also used as wound dressings to reduce scar elevation and pigmentation.
Glycerin
This natural moisturizing ingredients aids in repairing dry or cracked skin.
- Because of its ability to lock in moisture, using products with glycerin at night can keep your skin hydrated overnight.
Hyaluronic Acid
Possessing an exceptional capacity to retain water, hyaluronic acid plumps the skin and reduces the appearance of fine lines.
- It is also applied topically to promote wound healing.
Niacinamide (Vitamin B3)
Niacinamides, otherwise known as Nicotinamide or Vitamin B3, helps build keratin, keeping your skin firm and healthy.
- It also reduces inflammation, minimizes pores, and improves the skin barrier function (reducing transepidermal water loss).
- Topical application of Niacinamide was shown to improve the appearance of aged and photodamaged skin and a reduction in the appearance of hyperpigmentation
- In treating inflammatory acne, a study found nicotinamide 4% to be as effective as clindamycin 1% when applied topically twice daily for 8 weeks.
Oat Extract
Colloidal oat (Avena sativa) extract has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties, making it beneficial for redness and itching.
Panthenol
Panthenol, also known as Pro Vitamin B5, helps to improve skin hydration and reduce water-loss to maintain softness and elasticity.
Peptides
Peptides, short chains of amino acids, can help stimulate collagen production to improve the appearance of aging skin, such as fine lines, wrinkles and dark circles under the eyes.
Petrolatum
Petrolatum (more commonly known as petroleum jelly or Vaseline) is considered one of the most effective moisturizing ingredients.
- It creates a physical barrier on the skin's surface that helps trap moisture and prevent transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
- While effective for dry or chapped skin, it may clog pores and cause breakouts in some people.
Retinol
Retinol, a derivative from vitamin A, is less potent than its prescription counterpart, tretinoin.
- It stimulates collagen production, diminishes wrinkles, and improves skin texture, explaining its frequent presence in anti-aging products.
Squalene
Squalane is a component of the skin’s sebum which occurs naturally and is able to mix with the skin lipids, aiding the spreading of these lipids and helping to enhance the moisturising effect.
- As an occlusive component, squalane forms an external layer on the surface of the skin which helps to reduce TEWL while leaving the skin supple without a greasy feel.
Sulphur
Sulphur is a keratolytic, a mild antiseptic, a mild antifungal and a parasiticide.
- It has been used in concentration of up to 10% to treat acne, dandruff, seborrheic conditions, scabies and superficial fungal infections.
Thiamidol
Thiamidol, developed by Eucerin, works by reducing melanin production (the root cause of hyperpigmentation).
- It is clinically proven to reduce dark spots, and to reduce the reappearance of dark spots with regular usage.
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide is a mineral (physical) sunscreen that reflects ultraviolet light.
- It is often used with zinc oxide in physical sunscreen products.
Urea (Carbamide)
Topically applied urea has hydrating and keratolytic properties, hence improving the appearance of dry, rough or scaly skin.
- In managing ichthyosis and other dry skin disorders, it is applied in creams or lotions containing 5 to 25% urea; higher concentrations of 30% and 40% have also been used in severe cases.
- A preparation containing 40% may be used for nail destruction.
Vitamin C (L-Ascorbic Acid)
L-ascorbic acid is an antioxidant that works synergistically with vitamin E to protect against oxidative damage.
- It increases collagen synthesis, minimizing fine lines, scars and wrinkles.
- Additionally, it reduces pigmentation by reducing melanin formation, resulting in brighter skin.
Vitamin E (Tocopherol)
Vitamin E is an important fat-soluble antioxidant that protects the skin form UV damage and environmental stressors.
- It also promotes wound healing.
Zinc Oxide
Zinc oxide is mildly astringent and is used topically as a soothing and protective application in eczema and slight excoriations, in wounds, and for haemorrhoids.
- Additionally, zinc oxide reflects ultraviolet radiation, making it a physical sunscreen.
Summary
By understanding the science behind these essential ingredients, feel free to explore new products more confidently.
- However, remember not to fall prey to marketing gimmicks and always prioritize your skin's specific needs.
Nonetheless, even when containing similar active ingredients, the effectiveness of skin products can vary significantly.
- This is primarily due to differences in texture, formulation, and delivery technology, which all influence transdermal absorption.
- Some lesser-known products may simply be a mixture of ingredients with limited scientific testing or may even contain adulterants.
External Links
- Checking Ingredients Is Easy, Thanks to These 11 Websites, 2024
- Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications, 2017
- CosDNA
- EWG's Skin Deep
- INCI Decoder
- Understanding Popular Skin Care Ingredients, 2022
- Skincare Ingredients in CeraVe
- Ingredients in QV
- A Complete List of Common Skincare Ingredients & What to avoid
Comments
Post a Comment